FL Studio Mobile
SuperSaw
SuperSaw recreates two massive and classic synth sounds - Super Saws and Oscillator Sync. SuperSaw is a great synth to quickly create Electronic Dance Music style sounds including massive stereo pads and leads. Load the presets or create your own sounds from scratch. There are 7 main tabs covering the synthesizer controls:

Parameters
Oscillator
Oscillators are the sound source for the synth. There are two, mutually exclusive, Oscillator modes crating distinctive sounds, Supersaw and Supersync:
Supersaw:
Supersaw adds a number of Saw waves to create ripping leads and lush pads.

- Pulse Mode - When selected the oscillators generate Square Waves. When deselected, Sawtooth waves are generated.
- Pulse Width - When selected, the width of square wave can be modulated. NOTE: When set to 0%, the square wave width will be zero, effectively muting the oscillator. When set to 100% the oscillator is at the default, a normal square.
- Sub Oscillator - Level of the Sub Oscillator. The Sub Oscillator is a Saw wave, 1 octave below the current note.
- Unison - Unison is a thickening / stereoizing effect, similar to chorusing. Unlike chorus, that is applied to the final output, unison is a per-note effect where each note is given a user-defined number of 'subvoices' (from the Unison setting). Subvoices are then given user-defined variations of panning, pitch detune and phasing relative to the root note, as per the following controls:
- Detune Spread - Pitch variation (detune) across the unison voices. Causes interesting chorus/phase sounds. With Pan creates stereo motion.
- Unison Pan - Panning variation across the unison voices.
- Unison Phase - Starting phase variation across the unison voices.
- Detune Spread - The relationship between detuned voices. In the middle, the difference in pitch between the voices is linear. At minimum, more voices are clustered closer to the root note frequency. When maximized, detune voices cluster furthest from the root note.
- Retrigger - Voices reset phase with each note. When deselected, phase is random.
Supersync:
Supersync - A pair of oscillators, master and slave, work together. The master oscillator restarts the period of the slave oscillator, so that they will have the same base frequency. When the slave is at a different (lower) pitch to the master, it is abruptly cut off mid-cycle. This produces a sound rich harmonics and instantly recognizable. Use the oscillator 'Pulse mode', to create the classic sync sound.
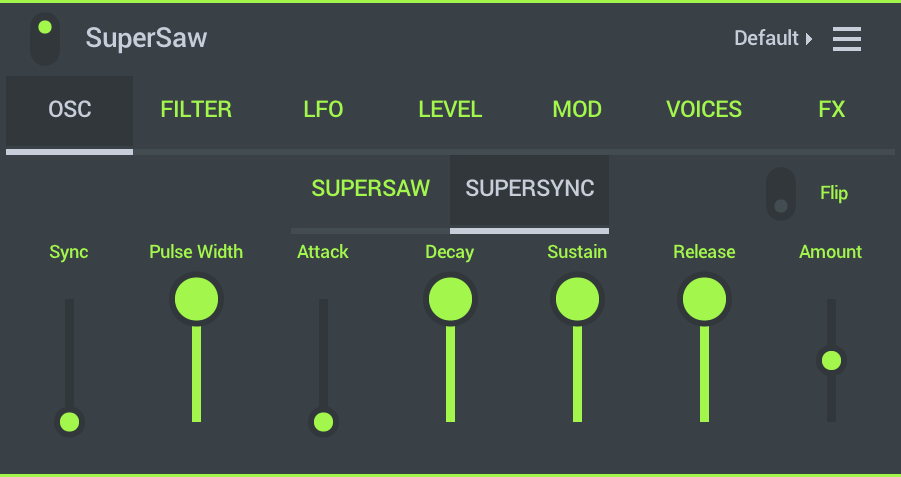
- Sync - Amount of oscillator sync effect. When set to minimum, the output is just a Pulse Wave. NOTE: Most effective when modulated by the EG or LFO > Destination > Oscillator Sync.
- Pulse Width - Minimum waveform width. NOTE: Most effective when modulated by the integrated envelope (Amount) or from the EG or LFO > Destination > Pulse Width control.
- ADSR - An envelope controlling:
- Attack - Time taken for the modulation to reach the maximum level.
- Decay - Time taken to go from the maximum level to the Sustain level.
- Sustain - Level when the key is held.
- Release - Time taken to fall from the Sustain level to zero when the key is released.
- Amount - Amount of envelope to modulation. Turn up positive modulation and down for negative modulation (-/+ 100%).
- Flip - Flips the Sync, 'Envelope Generator' direction depending of notes sequence: If previous note was higher than current note, the Sync EG Amount direction is reversed.
Filter
SuperSaw uses a single Low Pass filter with cutoff and resonance controls. Low Pass filters allow frequencies below the cutoff frequency to pass. When set to the highest frequency this means all frequencies can be heard. When set low, only the lower frequencies will be heard.
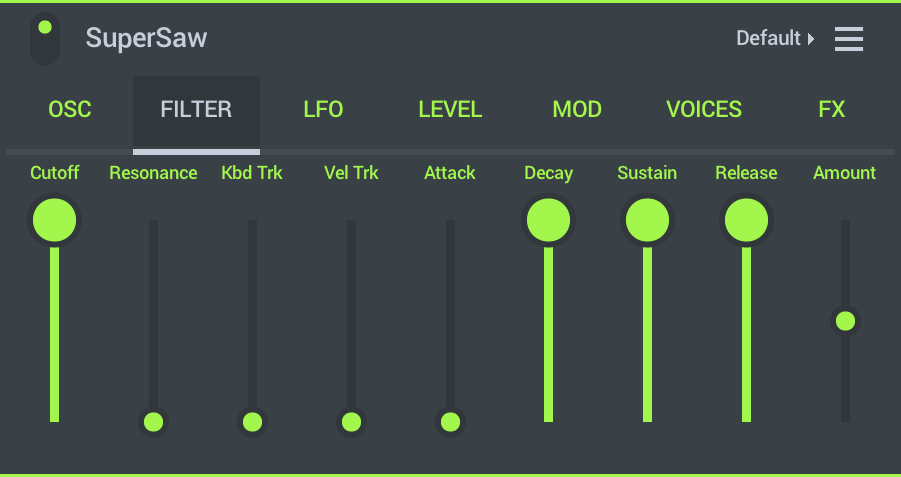
- Cutoff - Filter cutoff frequency (the filter is of the low pass type)
- Resonance - This causes a peak at the cutoff frequency that is most noticeable when the cutoff frequency is changed.
- Keyboard Tracking - Filter Cutoff frequency can be set to increase (up) or decrease (down) with keyboard position. This is useful to open or close the filter as you progress up the keyboard, so higher keys are brighter sounding for example.
- Velocity Tracking - Filter Cutoff frequency can be set to increase (up) or decrease (down) with note velocity. This is useful to open or close the filter as you change velocity. Higher velocities are brighter sounding for example.
- ADSR - An envelope controlling the filter cutoff amount. Attack. Decay. Sustain and Release parameters. To better understand ADSR controls it's useful to have in mind that for any note there are three basic timing events, 'note on', 'note hold time' and 'note off'.
- Attack - Time taken for the filter to reach the maximum level.
- Decay - Time taken to go from the maximum level to the Sustain level.
- Sustain - Level when the key is held.
- Release - Time taken to fall from the Sustain level to zero when the key is released.
- Amount - Amount of envelope to filter cutoff modulation. Turn up for positive modulation and down for negative modulation (-/+ 100%).
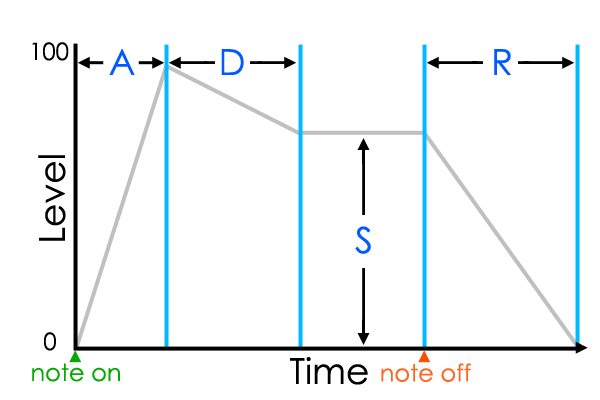
ADSR Diagram
- Amount - Amount of filter applied as per the envelope settings.
Low Frequency Oscillator (LFO)
LFO's are a modulation source that can be used to create interesting effects by slowly varying the values of other parameters.
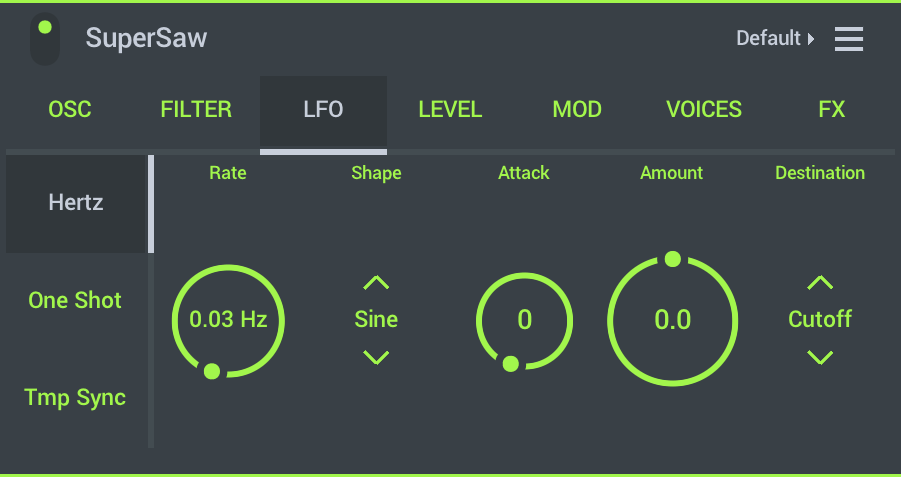
- LFO Mode - There are three options:
- Hertz - LFO varies constantly at the Rate set in Hertz (cycles per second).
- One Shot - LFO cycles once at the Rate set in Hertz (cycles per second).
- Tempo Sync - LFO varies constantly at the Tempo set in Beats. It is also synchronized with the current Beat number.
- Rate - Frequency of the LFO waveform. This can be FREE-running or tempo synced (TMP). When Tempo Sync is selected you can select tempo based delays.
- LFO Shape - Shape of the LFO waveform. Choose from:
- Sine - smoothy varying wave shape.
- Saw - sharp attack and linear decay, like a 'Saws teeth'.
- Square - flips between two states.
- Random - Random values.
- Attack - Attack time for the LFO modulation to start (fade-in).
- LFO Amount - Amount of LFO to destination modulation. Turn right for positive modulation and left for negative modulation (that is to invert the waveform, -/+ 100%).
- LFO Destination - Choose the modulation target of the LFO waveform:
- Cutoff - Filter cutoff frequency.
- Resonance - Filter resonance amount.
- Frequency - Oscillator pitch or tune.
- Oscillator Sync - Oscillator sync modifier.
- Pulse Width - Oscillator Pulse Width modifier.
- Unison Detune - Oscillator Unison voice detune modifier.
- Level - Oscillator unison voice level.
- Pan - Oscillator unison voice pan.
Level (Master Volume Envelope)
Oscillator Envelope controls. The ADSR envelope provides a volume envelope (volume changes) at key on, key held and key release. These controls are how you would make a note play on after you release the key or to soften the attack of a sound, for example.
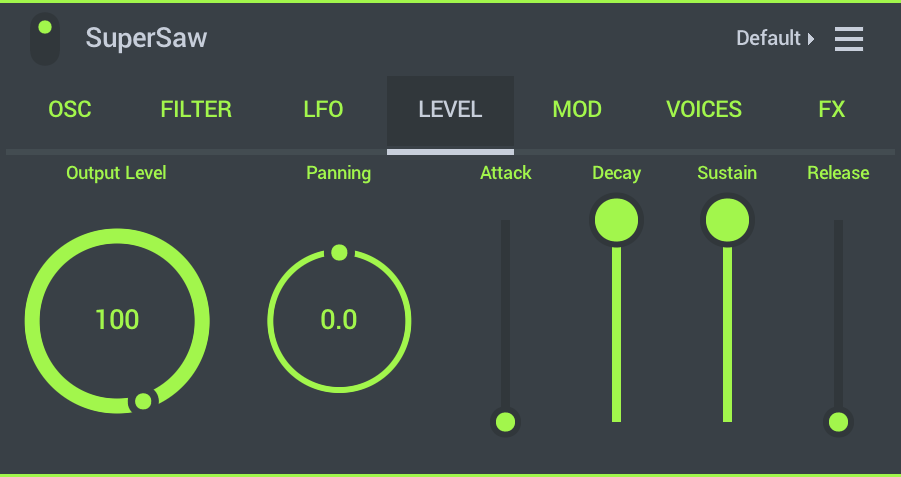
To better understand ADSR controls it's useful to have in mind that for any note there are three basic timing events, 'note on' event, 'note hold time' and 'note off' event.
- Output Level - Per voice volume level.
- Panning - Position of voices in the stereo field (Left/Center/Right).
- Attack - Time taken to reach the maximum level.
- Decay - Time taken to go from the maximum level to the Sustain level.
- Sustain - Level when the key is held.
- Release - Time taken to fall from the Sustain level to zero when the key is released.
ADSR Diagram

MOD (Modulation)
This tab sets the Pulse Width Modulation amount and assigns modulation targets to the ModWheel as found on the Touch Keyboard.
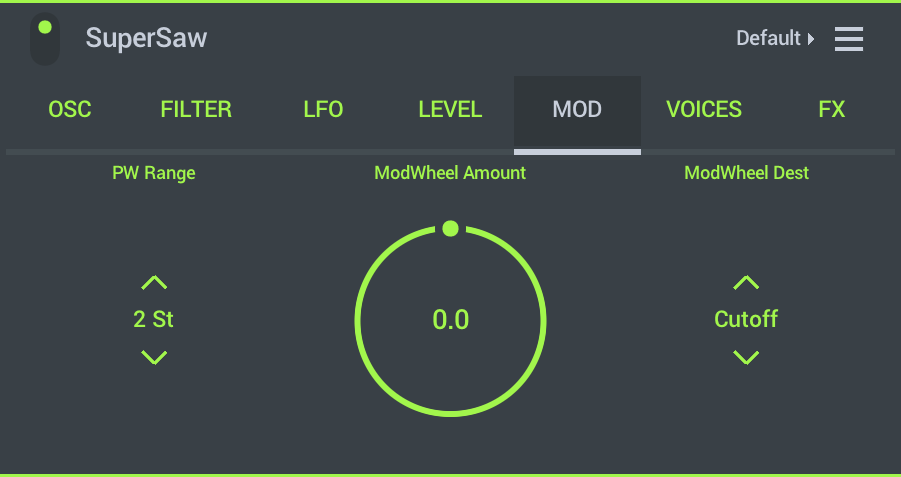
- PW Range - Pitch Wheel range in Semitones.
- ModWheel Amount - Assign the Keyboard MOD wheel to positive (right) or negative (left) modulation.
- ModWheel Dest - Destination for Modwheel user selected modulation:
- Cutoff - Filter cutoff frequency.
- Resonance - Filter resonance amount.
- Oscillator Sync - Oscillator sync modifier.
- Pulse Width - Oscillator Pulse Width modifier.
- Unison Detune - Oscillator Unison voice detune modifier.
- Level - Oscillator unison voice level.
- Pan - Oscillator unison voice pan.
- LFO Amount - LFO amount, as assigned to its destination.
- LFO Rate - LFO speed, as assigned to its destination.
Voices
Oscillator Voice controls:
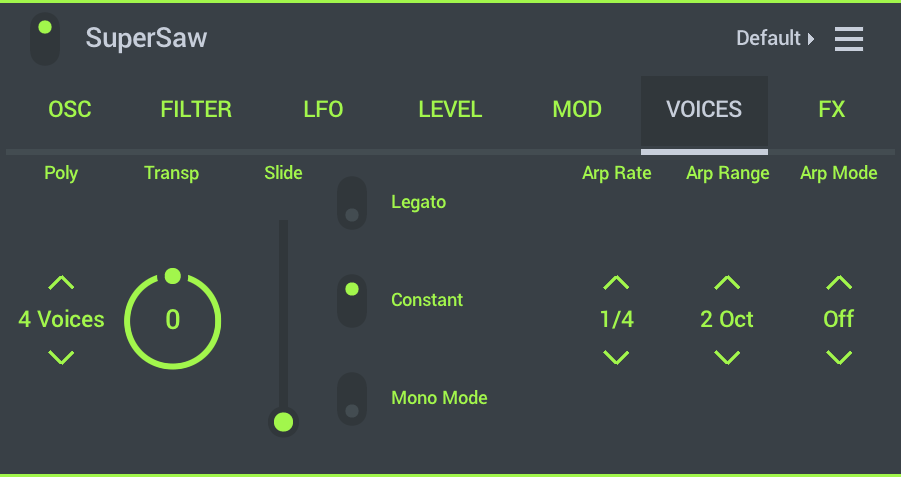
- Polyphony - Maximum number of voices that can play. Useful when fast arpeggios play notes with long decay times. This stops too many notes building up and overloading your CPU.
- Transpose - Change the pitch in semitones.
- Slide - Slide time. Slides will be initiated with overlapping notes only if Legato Mode is enabled.
- Legato - Only overlapping notes will slide.
- Constant - Constant slide time regardless of slide distance. When this is off, larger slide intervals will take longer.
- Mono Mode - Monophonic (1 note). Only one note will play at a time. When this is off chords will be played and new notes (when held) will slide.
- Arpeggiator controls:
- Arp Rate - Set the speed according to tempo options.
- Arp Range - Octave range over which the Arpeggiator spans.
- Arp Mode - Set the Arpeggiator pitch direction the arpeggiator cycles. NOTE: 'Up/Down 2' will repeat the last and first note while 'Up/Down' will only play these once.
Effects (FX)
There are two integrated effects. Distortion and delay.

- Distortion - Amount of Guitar/Amplifier style distortion.
- Gain - Set the post-distortion level. Use to control the volume as high distortion can also make the synth much louder.
- Delay - controls include:
- Time - Delay time according to tempo units (BPM).
- Delay Feedback - Number of echoes.
- Delay Filter - Amount of high frequency filtering applied to each round of echoes.
- Delay Mix - Echo volume.