MIXING & EFFECTS
Audio Input/Output Routing
This section covers internal Mixer audio routing functions. Internal audio sources (instruments loaded in the Channel Rack) are routed to the Mixer insert tracks with the Channel settings FX selector, as shown below:
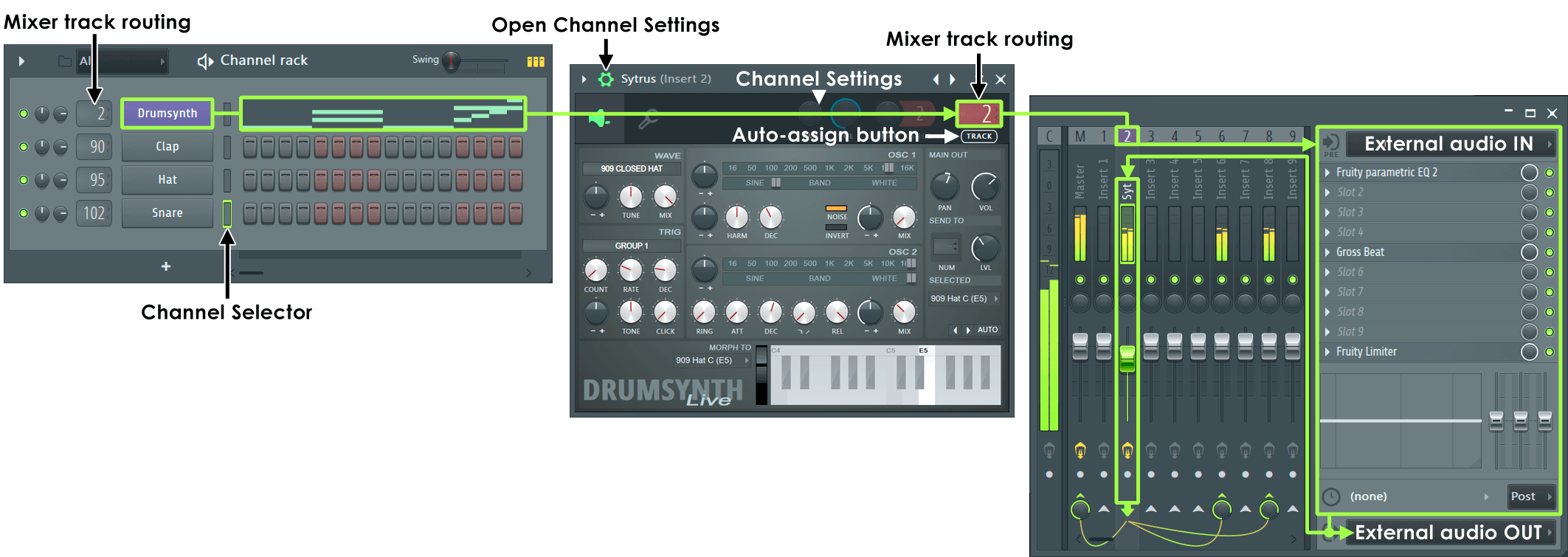
NOTE: In the example above Mixer Track 2 is selected and so the Track Send switches, External audio Input / Output options and Mixer Track Properties change to show unique settings for Mixer track 2. Usually the only Mixer track with an external audio output is the Master Mixer track.
Some points about internal and external audio routing:
- Routing instruments to Mixer tracks - See Routing Instrument Channels to Mixer Tracks.
- Internal sends and sidechan sends - See Internal Mixer Track Routing & Sidechaining.
- External routing - Audio sent to and received from your audio devices input and output jacks is set by the External audio IN / OUT selectors (as shown above). NOTE: that each Mixer track has its own input and output options. For example, if you have an audio device with 16 microphone inputs, then you have the option of setting 16 unique Mixer tracks to receive each of these audio device inputs. It is even possible to set two or more Mixer tracks to receive the same input or send to the same output. When '(none)' is shown, this means no external audio device input or output is selected for the selected track. By default, the Master Mixer track 'Output' is the routed to the audio devices main outputs (usually the main/front Left/Right channels). However, by routing another Mixer track (other than the master) to other audio devices outputs (e.g. the rear channels of 5.1 surround-sound card), you can create a separate sub-mix for band headphone monitoring or studio monitoring.
- Parallel internal / external routing - It is worth noting that the Mixer track External audio IN / OUT can function in parallel with the internal routing functions so that any track can receive external and internal audio sources simultaneously OR output to the Master Mixer track and any other available audio device output. Mixer routing is described in more detail below:
How to Route Audio
- Mixer tracks - can take an input audio signal from one or more internal Instrument Channels by setting the Mixer Track Selector to a given track OR one external source (External audio OUT). After processing the input they can pass the audio to another location, usually the Master track (M) but it can be another Mixer track (as shown by the cables) or directly to a audio device output (External audio OUT).
- To send audio from one insert track to another - Select the source track you wish to send FROM and then Left-click the send control switch
 on the destination track you want to send TO. A send-level knob will appear on the destination track that can be used to change the level of signal passed to the destination. By default the SOURCE track will maintain routing to the Master track - If you don't want to create a parallel path to the Master Mixer track, select the source track and disable the send switch on the master by Left-clicking it.
on the destination track you want to send TO. A send-level knob will appear on the destination track that can be used to change the level of signal passed to the destination. By default the SOURCE track will maintain routing to the Master track - If you don't want to create a parallel path to the Master Mixer track, select the source track and disable the send switch on the master by Left-clicking it.
- External Inputs - Most ASIO drivers provide inputs (External audio IN) for microphone, line-in, etc. You can route these inputs to any or all Mixer tracks. Note that the ASIO inputs will not replace but mix together with any input audio the track receives from other sources (instruments, other tracks, etc).
- External Outputs - Most ASIO drivers provide outputs (External audio OUT). You can route any Mixer track to any ASIO output.
- Surround sound 5.1 or 7.1 - You can set a group of Mixer tracks to output (External audio OUT) to the individual channels of a 5.1 surround system for surround-sound mixing. A Surround sound template is available in the File menu > New from template > Utility > Surround panner. After opening this template, select audio device outputs using the Output menu to match the pre-named Mixer tracks.
- FL Studio as VST - Additional outputs also appear when using the FL Studio multi output VSTi connection.
Limitations of routing:
- If you are using the 'Primary Sound Driver' audio driver only one track at a time can output to the primary output (usually this is the Master Track). This limitation does not apply if you use an ASIO driver, then any Mixer track may be routed to any available output.
- FL Studio will disable routing options that would create a feedback loop (for example trying to route a track to itself).
- Use the Send Level knobs to adjust the amount of signal sent from an insert track to the send tracks.
- The specially named 'Current' track can only receive audio from the currently selected track. Its main purpose is to hold an Edison plugin, ready to record any selected tracks audio OR visualization plugins, such as WaveCandy.
Prepare for Recording
The record arm switch prepares a track for audio recording (to a *.wav file). The input and/or any internal audio routed to that track will be recorded.
Mixer reference diagram
See the main Mixer page for a full description.
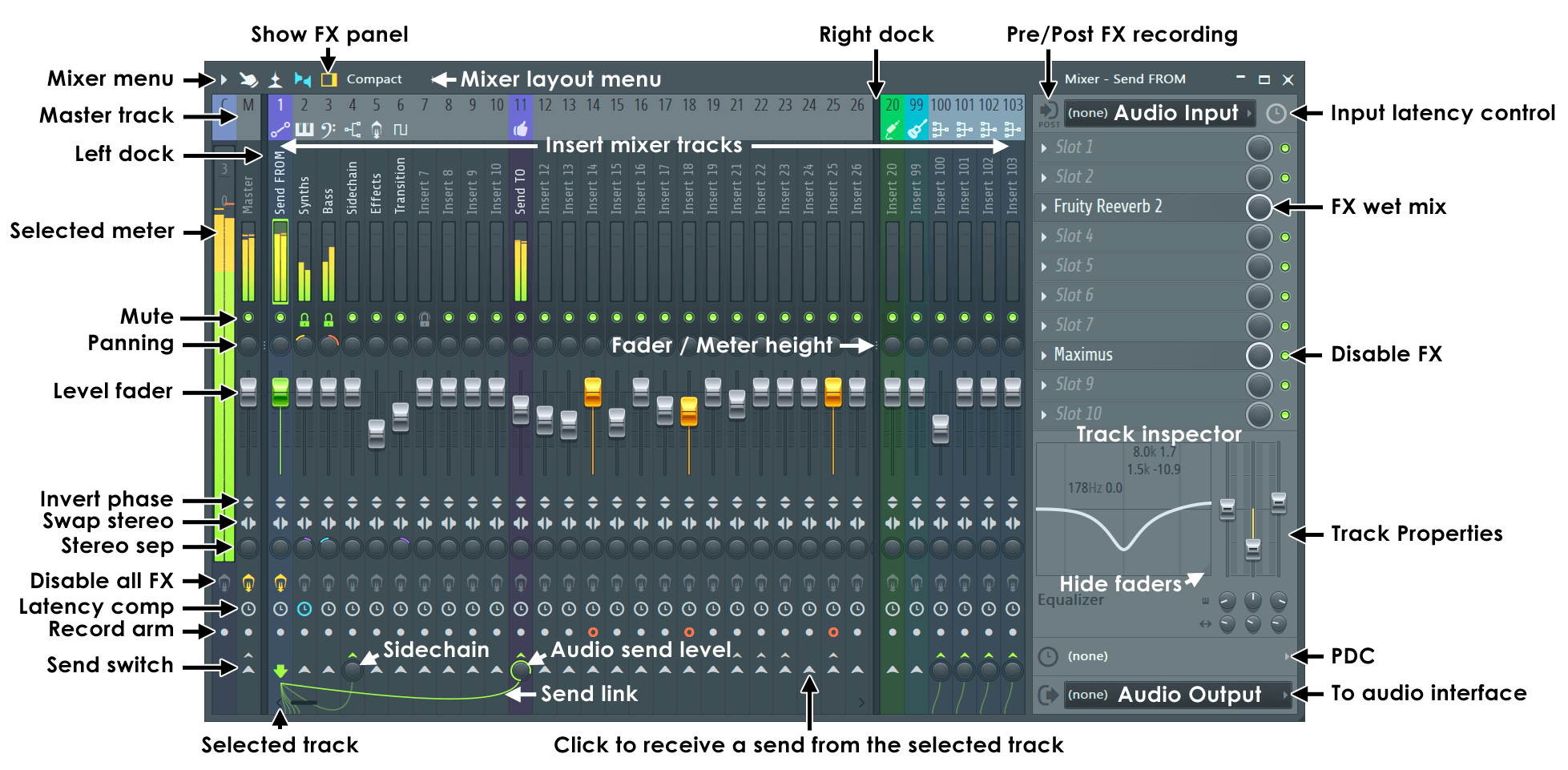
NOTE: Most controls are automatable (Right-Click and select 'Create automation clip').